Spotting Oil and Gas Equipment Problems Before They Occur

The oil and gas sector is one of the most important industries that fuels global economies. The industry uses complex equipment across the entire supply chain, starting from extraction. However, this equipment is not immune to failure or breakdown, especially when it operates in challenging conditions, such as high pressures, high temperatures, abrasive particulate matter and caustic chemicals. Spotting oil and gas equipment problems before they occur can help organizations avoid worse damage to the equipment, accidents and losses.
In This Article
- Levels of Equipment Failure
- Common Machinery Problems in the Oil and Gas Industry
- Signs of Oil Pump Failure
- Equipment Inspection and Care
- Replace Bad Equipment With High-Quality Products
Levels of Equipment Failure
Problems in oil and gas equipment can lead to severe safety, environmental and health consequences. Before problems happen, define the degree of failure to establish the right approach to investigating why the problem occurred and how to spot similar problems in the future. For example, learn the signs of oil pump failure to prevent future oil pump failures.
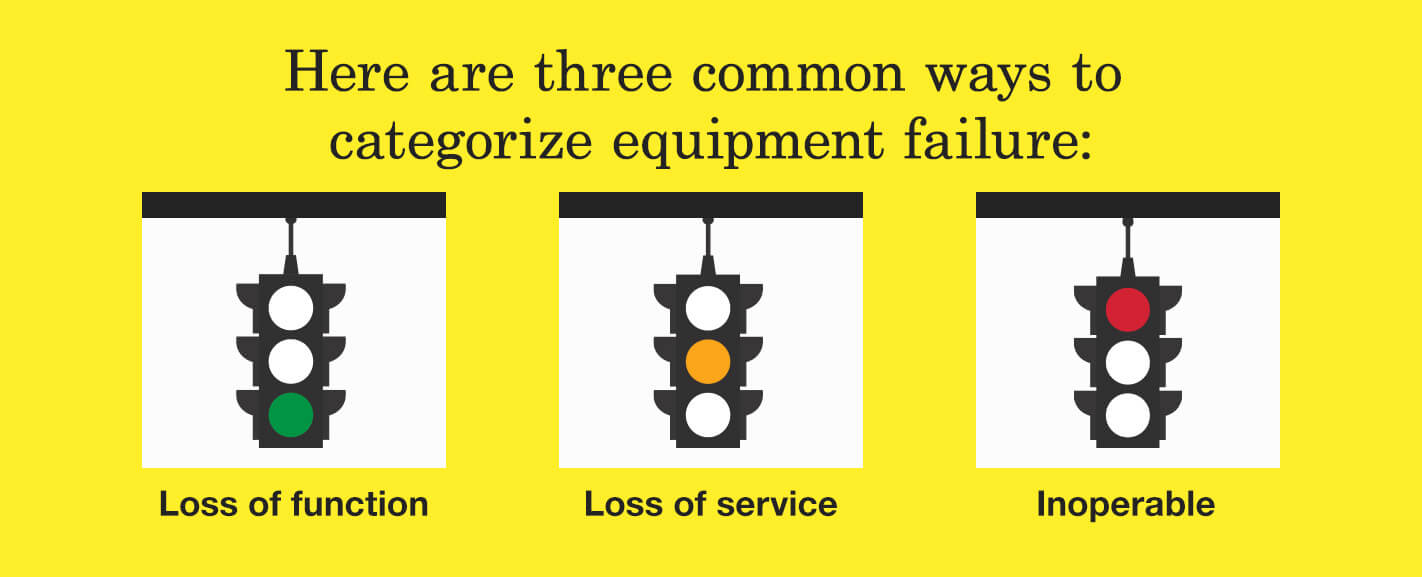
Equipment failure can be defined in varying levels of severity. Here are three common ways to categorize equipment failure:
- Loss of function: At this level, a system or component works but doesn't perform its intended function.
- Loss of service life: This level of failure means a system or component can still do the job but is unsafe or unreliable.
- Inoperable: At this point, a system or component becomes inoperable.
Understanding the root cause of each problem is critical so you can take action to prevent its reoccurrence. Failure analysis, which can be complex and involve several laboratory, observation and inspection techniques, can detect these problems and determine the root cause of failure.
Common Machinery Problems in the Oil and Gas Industry

Equipment in the oil and gas industry must run efficiently and safely for businesses to succeed. Failure in machinery can lead to downtime, decrease efficiency and cause safety concerns. To spot these equipment problems before they occur, you must first be able to identify the issues, then you can follow a plan for rapid replacement or maintenance. This section explores some of the most common equipment issues in the oil and gas sector.
Corrosion and Wear
The oil and gas sector operates in environments that can be extremely harsh. These conditions can be due to exposure to high temperatures or corrosive chemicals. In addition, continuous use of these machines may harm the equipment body and housing, as well as crucial parts of the machinery such as valves, pumps and pipes. If not checked regularly, these machines may break down, leak or pose serious hazards to the people operating them.
Implementing routine inspections, maintenance and timely replacement of worn-out parts can help prevent serious wear and tear. Check for signs of wear and tear, and schedule regular maintenance to extend the equipment's life span. Predictive maintenance technologies can also help reduce the impact of wear and tear.
Fluid Problems and Contamination
Lubricants and hydraulic fluid can get contaminated due to dirt, water and debris. The contamination can inhibit the equipment's performance and reliability or even damage it. A sign of water contamination in hydraulic fluid is a milky appearance. One of the sources of this contamination is condensation buildup on the walls of the fluid reservoir caused by changes in temperature from warm days to cool nights. Water contamination can cause corrosion of the pump and other essential components of the equipment.
Air bubbles can also contaminate the fluid and result in knocking or banging noises. These noises are due to the compression and decompression of air as it moves through the system.
Most contaminants are small, and you must have control measures to catch them at all levels, including regular fluid analysis, appropriate storage practices and a stringent filtration system. In addition, you should only use high-quality lubricants and fluids to maintain the performance and integrity of the equipment.
Misalignment From Vibration
Equipment can vibrate and become misaligned. Vibration issues are common in compressors, pumps and turbines, leading to bearing failures, premature wear and damage to the machine's structure. Extreme vibration and misalignment can cause severe damage.
Regular vibration analysis, proper alignment and balancing are crucial to ensuring the equipment is more efficient and has a longer life span. Predictive maintenance and vibration analysis can also detect potential vibration problems, allowing organizations to make informed corrective measures.
Instrument and Electronic Failures
Sensors, monitors and control systems are crucial in the smooth operation of machines. Failure in these components can hamper the reliability of the equipment. Power surges and moisture ingress are the main causes of problems in instruments and electronics. Sudden bursts of electrical discharge can cause damage to electronic components.
Inspect and maintain these systems regularly to ensure they do not break down. Consider using surge protectors to prevent problems caused by electrical discharge.
Operator Error
Operator errors occur when employees make mistakes while operating the equipment. Lack of attention, improper or insufficient training, misinterpretation of operating instructions, and negligence can contribute to machine failure or accidents. Clear operational guidelines and sufficient training are crucial to minimizing operator errors. Invest in ongoing training to ensure staff are always updated on proper machine operation methods. Encourage a culture of open communication that makes it comfortable for employees to express themselves and communicate their challenges when operating the machines.
Signs of Oil Pump Failure
Oil pumps keep all machinery components well-lubricated to minimize friction and wear and tear. A well-functioning oil pump ensures the machine operates efficiently and can extend its life span. To avoid scenarios where the pump fails and compromises the equipment's performance, you need to know the signs to look out for when an oil pump breaks down or fails.
Check for the following signs of oil pump issues:
- Insufficient oil pressure: Low oil pressure cannot move the oil to all parts of the machine it's supposed to lubricate. Oil leaks may cause low pressure, so ensure a sufficient supply to generate enough pressure to move the oil to all parts requiring friction protection. Most lubricating systems have an oil gauge that indicates if the oil pressure is adequate for the machine. If this gauge is unavailable, you should buy a pressure measuring instrument to test and monitor the oil pressure. Operators of the machine or repair technicians should know how to test an oil pump to ensure the equipment is always well-lubricated.
- High equipment temperature: One of the common problems with oil pumps in the oil and gas industry is increased temperature. A temperature rise indicates increased friction, which means the machine is not well-lubricated. The solution is to ensure there is enough oil. Proper lubrication reduces the temperatures by absorbing the extra heat generated by the machine and releasing it as the oil flows around other components. In addition, by reducing friction, oil prevents the rise in temperatures.
- Noisy hydraulic lifter: The hydraulic lifter is an important part of the valve train function of certain components. It helps maintain valve clearance. The hydraulic lifter needs regular, sufficient lubrication to perform properly. Insufficient oil will cause friction, which results in noise. Ensure you understand hydraulic system problems and solutions to ensure the hydraulic lifter is always at its peak performance. Checking oil level and pressure can help you troubleshoot a noisy hydraulic lifter.
- Noisy valve train system: Insufficient oil supply can also cause other components of the valve train system — besides the hydraulic lifter — to make noise. The noise could be a sign of the oil pump failure. Stop operating the machine when you hear noise produced in the valve train and investigate further to establish any malfunctions in the oil pump.
- Noisy oil pump: An oil pump in good condition should operate quietly. Any noise, whether produced in the valve train system or from any other part of the pump, could be a sign that it's failing. For example, the wearing of gears may produce a winning noise.
Most oil pump problems result from low levels or inadequate amounts of oil, which causes low pressure, friction and malfunctioning in other parts of the equipment that don't get lubricated.
The oil pressure gauge or sensor measures oil pressure to detect problems in the pump. If the pressure is low, equipment parts are not well lubricated. However, a defective oil pressure gauge will not accurately measure the oil pressure. An incorrect oil pressure gauge reading is one of the major signs of a bad oil pump sensor.
Equipment Inspection and Care

Oil and gas equipment must always perform at their peak to ensure profitability and protect the environment. To maintain this performance, maximize working life span and maintain regulatory compliance, organizations in the oil and gas industry must conduct regular inspections. These inspections will allow your team to detect problems and implement solutions.
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is the most effective means of testing oil and gas equipment. This approach allows technicians to inspect the machine without taking it out of service. Common NDT inspection techniques include:
- Visual inspection: A trained and experienced technician can detect corrosion development, improper structural installations, welding flaws, cracks and impending structural failures by close visual inspection. It is the industry's first and most common inspection method and is inexpensive compared to other NDT inspection techniques. However, the human eye can only see so much.
- Radiography: Radiography uses X-ray or gamma rays to examine a machine's internal structure and integrity. The rays can travel through steel and metallic alloys. This inspection technique is used to inspect welds on pipelines and pressure vessels. It can also be used to inspect non-metallic materials like ceramics and concrete.
- Liquid penetrant testing: This technique is mainly used to detect leaks and cracks. A dyed liquid is applied to the investigated area to reveal areas the liquid can seep into.
- Ultrasonic testing: This NDT technique utilizes waves with frequencies above the human ear's audible range. It is portable, versatile and accurate. The acoustic waves are transmitted to solid objects, then the return waves are analyzed. Ultrasonic testing can detect volumetric damage or defects, including corrosion and voids.
- Thermography: This technique detects temperature changes in pipelines by measuring the difference between the pipeline's temperature and the surrounding environment. It helps detect defects in pipeline insulation and oil or gas leaks.
In addition to the NDT techniques, companies in the oil and gas industry conduct lifting and tabular inspections. Lifting inspection ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations and prevents injuries or accidents caused by damaged lifting equipment. Inspect lifting equipment such as hoists, cranes and other lifting devices for signs of wear to ensure they remain safe to use. Tabular inspection examines metallic tubes for faults like manufacturing flaws and corrosion.
An inspection checklist helps ensure you don't miss any important checks on the machines and other related issues. The checklist should have the following:
- Safety equipment inspection: Check the availability and condition of safety equipment to ensure workers can use it when needed. Safety equipment includes fire extinguishers, eye wash stations, personal protective equipment and safety showers.
- Equipment maintenance: Perform maintenance regularly to prevent breakdowns and expensive repairs.
- Hazardous material handling: Ensure hazardous materials are handled and stored properly.
- Training and competency: All staff should be trained to operate the machines properly.
- Emergency response plan: The organization should have an emergency response plan.
- Facility cleanliness: Ensure the facility is clean.
- Environmental controls: Regularly inspect environmental controls such as emission controls and waste management.
- Compliance with regulations: Ensure you stay compliant with relevant standards and regulations.
Replace Bad Equipment With High-Quality Products
Inspection and maintenance are critical to ensuring oil and gas equipment remains efficient and safe. Replacing worn parts is the solution to some defects or damage. If a specific machine keeps on breaking down despite the regular inspection, maintenance and repairs it undergoes, it's time to replace it to avoid downtimes. The replacement should be of high quality and durable to ensure a long life span and minimize disruptions in operations.
Use high-quality products from Global Elastomeric Products to replace damaged or defective equipment parts. We are a global oilfield supplier of elastomer products for industrial use. We have over 50 years of experience in the industry and offer a large variety of products and capabilities for almost any application. Contact us for more information.





